Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) in Secure Hyper Text Transmission Protocol (HTTPS)
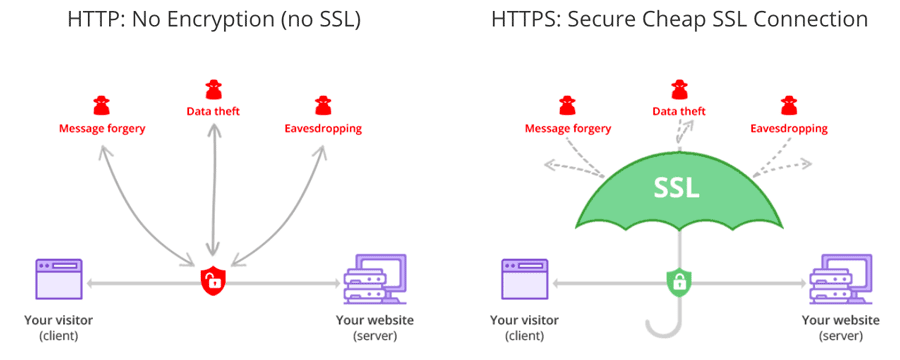
Secure Hyper Text Transmission Protocol (HTTPS) is an improved version of Hyper Text Transmission Protocol (HTTP) for web and internet browsing data transmission. It is coupled with a main security feature: Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) in the HTTPS protocol which is integrated with all existing HTTP response codes.

This article is about the Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) security feature embedded in HTTPS as part of the HTTPS protocol.
The SSL is a computer network security mechanism in the forms of a protocol and network software program for authentication of identity between its applied users (hosts) and encryption of its data transmitted.
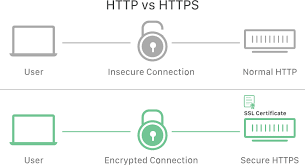
SSL authenticates the identities of its applied users and computer hosts with an SSL certificate to verify any true and legitimate identity of its certificate owner. This certificate is published on an SSL user’s and host’s computer system to the world wide web and any internal non internet network.
It contains the identity and address details of its published host computer system, which is also embedded with its computer system’s SSL public key. More on this in the coming.
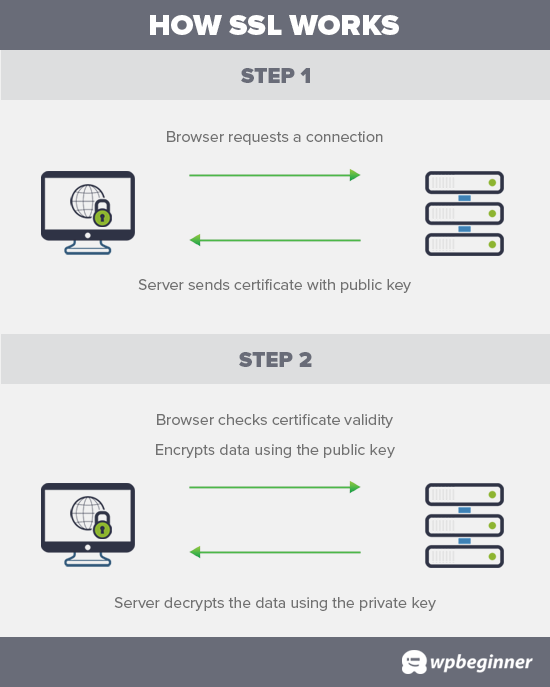
SSL utilizes two different keys per computer host system. A public key, and a private key. The public is shared and published in every SSL certificate for any other computer node in a network to identify, validate and authenticate to the identity and its details of a host computer system.
The private is secret and personal, so thus private to its computer host system.
As such, during encryption of data in network transmission between SSL users and computer hosts, the public key of a computer host system is used to encrypt data by its corresponding transmitting party, while the private key of the computer host system is used to decrypt this data.
Inversely, for SSL digital signatures and signing, a computer host system’s private key is used to encrypt (sign) the data and the public key of the same computer host system is used to decrypt the data. Therefore, the plaintext acquired from the data transmitted can be matched against any differences in the integrity of the data.
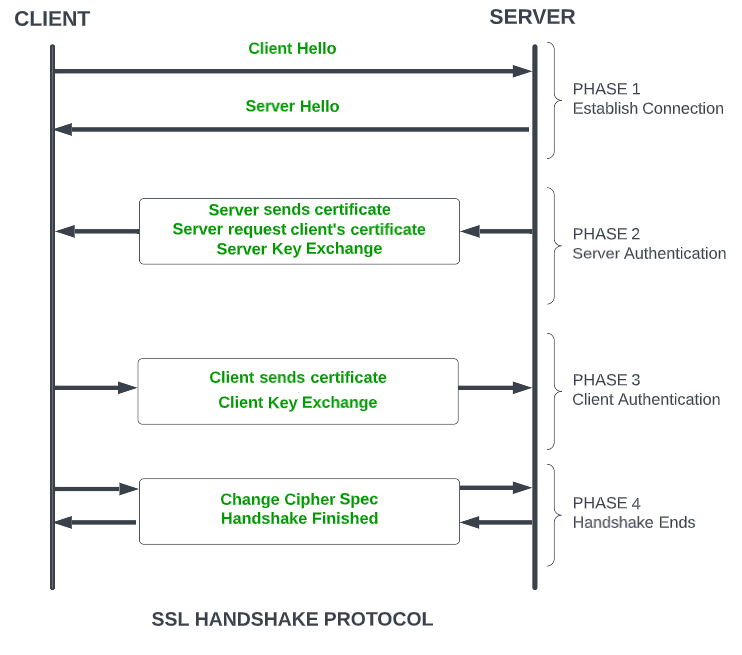
To conclude the point of this way to encryption and digital signing with a public key and private key is verified by the SSL certificate to validate the identity of any SSL user and computer hosts for trusted and legitimate connections to data transmissions between SSL users and computer hosts.
P.S. The “Change Cipher Spec” explained in the diagram above is to negotiate the encryption algorithm for SSL used between client and server, based on the available software program of the SSL protocol hosted by the server, and which is available on the client.
Finally, this way of encryption is also known as asymmetric cryptography and Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) cryptography.
More in the following are some perks and cyber security guards of SSL: